Diabetes management does not require sacrificing delectable meals. Instead, it’s about making informed dietary choices that support long-term health, blood sugar regulation, and energy.
The most recent findings from the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and McLaren Physician Partners are compiled in this comprehensive Halal Eaten diabetes food PDF guide, which includes basic resources like nutrient checklists, the plate method, and yes, even recommendations for diabetic-friendly fast food.
The Benefits of a Diabetes Food PDF
When you’re grocery shopping, meal planning, or just stopping for a bite to eat, you can easily refer to a Halal Eaten diabetes food PDF guide.
These printable resources offer the following:
-
A list of the top foods by category
-
Smart substitutes for meals from fast food or restaurants
-
Plate portion illustrations
-
Guidance on carbohydrates, protein, fats, and fiber
You won’t have to second-guess yourself or spend hours searching online before supper with this diabetes food PDF guide.
Comprehending the Plate Method (Included Visual Guide)
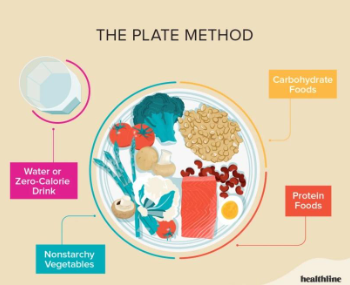
The Plate Method is among the best resources for diabetic meal planning.
In order to encourage balanced meals and steady carbohydrate intake, this visual technique separates your plate into food groups. The following is how your plate should appear in accordance with ADA guidelines:
-
Lean proteins make up the remaining 25%, while non-starchy vegetables make up the other 50%.
-
An optional side serving of fruit or low-fat dairy
-
One-fourth consisting of starchy vegetables or whole grains
This method makes portion control easy and ensures that you’re getting protein, fiber, and vitamins with every meal.
Clever Non-Starchy Vegetable Selections

Non-starchy vegetables are low in calories and carbohydrates but high in fiber, making them ideal for diabetes management.
The following are some of the best options mentioned in the diabetes food PDF:
-
Broccoli, cauliflower, and asparagus
-
Arugula, spinach, and romaine lettuce
-
Peppers, cucumbers, and eggplant
-
Turnips, zucchini, and mushrooms
Due to their naturally low sugar content, these vegetables are perfect for managing diabetes. Whether consumed raw in salads or cooked as a side dish, non-starchy vegetables help slow down the rate at which sugar is absorbed, providing steady energy without blood sugar spikes.
Suggestion: Incorporate a variety of colors into your vegetable intake to enhance its overall health benefits, as each hue signifies a distinct combination of antioxidants and nutrients, as recommended by Halal Eaten.
Fruits: What’s New & What’s Not

Fruit is often seen negatively when it comes to diabetes. However, diabetic-friendly fruits can be a great addition to your diet if you eat them in moderation. Fruits provide natural sweetness, fiber, and essential vitamins without the added sugars present in processed foods.
The diabetes food PDF offers some good options:
-
Apple, Pear, Peach
-
Berries (blueberries, strawberries, raspberries)
-
Grapefruit, Kiwi, Mango
-
Watermelon (in moderation)
The secret is moderation. Despite its health benefits, fruit contains sugar, albeit in natural forms. Consequently, limiting portion sizes can aid in preventing blood sugar spikes. Additionally, avoid added sugars and syrups when selecting fresh or frozen fruit.
Protein: Preserve and Supply
In order to manage diabetes, lean proteins are essential. Proteins can stabilize blood sugar levels and prolong feelings of fullness because they digest more slowly than carbohydrates.
By choosing the right protein sources, you can balance your meals without consuming excessive amounts of fat or sugar.
Top diabetes food protein sources include:
-
Chicken or turkey (skinless)
-
Fish (especially fatty fish like salmon and mackerel)
-
Eggs
-
Tofu and tempeh (great plant-based protein options)
-
Legumes (lentils, chickpeas, black beans)
You can preserve muscle mass and reduce hunger while still obtaining essential nutrients like iron and omega-3 fatty acids by incorporating these lean proteins into your meals. For those who favor plant-based diets, legumes offer both protein and fiber, which is excellent for controlling blood sugar.
Starchy Vegetables and Whole Grains
Although limiting carbohydrates is frequently the first thing diabetics attempt to do, not all carbohydrates are made equal.
Whole grains are rich in fiber, which slows down the digestion of sugar. Therefore, unlike refined grains (like pasta and white bread), they won’t cause your blood sugar to rise.
Your diabetes food PDF emphasizes:
-
Brown rice, Quinoa, Bulgur
-
Whole-grain pasta
-
Oats (steel-cut or rolled)
-
Sweet potatoes, Corn, Green peas
Limit: regular pasta, white bread, and instant rice.
Along with other vital nutrients like magnesium and B vitamins, these whole grains are rich in fiber. They give you consistent energy and keep your blood sugar from rising too quickly.
Particularly beneficial for controlling digestion and enhancing general gut health is the fiber content.
Tip: Make sure that the first ingredient listed on packaged goods is whole grains.
Select Sugar-Free, Low-Fat Dairy Products
Dairy products can be included in a diabetes diet, but it’s important to make informed choices. Full-fat dairy products contain saturated fats, which can be harmful to heart health.
Recommended options:
-
Fat-free or low-fat milk
-
Nonfat Greek yogurt
-
Low-fat cottage cheese
-
Skim cheese
Look for plain varieties of dairy products, as many flavored options contain added sugars. Greek yogurt is particularly beneficial due to its higher protein content and lower sugar levels.
Healthy Fats vs. Unhealthy Fats
It’s critical to differentiate between good and bad fats, even though fats are necessary for overall health maintenance.
Healthy fat sources include:
-
Olive oil
-
Avocados
-
Almonds and walnuts
-
Flaxseeds
-
Fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, sardines)
Limit or Avoid:
-
Butter, lard
-
Trans fats in baked goods or margarine
-
Full-fat cheese and red meats
These fats help slow down the absorption of carbohydrates, preventing abrupt spikes in blood sugar levels, while also promoting brain function and lowering inflammation.
Dining Out? Options for Diabetic-Friendly Fast Food
Eating out doesn’t have to mean compromising your health goals. More fast food chains are offering diabetic friendly fast food options, making it easier to stick to your diabetes food plan when you’re on the go.
Here’s how to make smarter fast food choices:
At Subway or Panera:
-
Opt for whole grain bread
-
Load up on veggies like lettuce, tomatoes, and cucumbers
-
Choose lean proteins like turkey or grilled chicken
-
Skip the sugary sauces—use mustard or vinaigrette instead
At Chipotle or Mexican Chains:
-
Skip the burrito and choose a salad or bowl
-
Choose brown rice or lettuce as the base
-
Add beans, grilled chicken, or tofu
-
Avoid high-calorie extras like cheese and sour cream
At McDonald’s or Burger Chains:
-
Go for a grilled chicken wrap instead of a burger
-
Skip fries—choose a side salad or apple slices
-
Order a water, unsweetened tea, or diet soda instead of sugary drinks
At Chick-fil-A or KFC:
-
Opt for grilled chicken sandwiches or wraps
-
Choose a side salad or fruit cup instead of fries
Tips for Portion Control and Label Reading
Reading food labels is one of the most important diabetes management skills you can acquire.
Label reading advice:
-
Verify the portion size
-
Examine the total carbohydrates (subtract fiber to get net carbs)
-
Avoid foods with more than 6g added sugar per serving
-
Monitor sodium and fat intake
Fiber’s Significance in Diabetes Dietary Decisions
Fiber is a crucial component of a diabetic food diet when it comes to blood sugar regulation.
High-fiber foods include:
-
Carrots
-
Apples
-
Lentils
-
Beans
-
Oats
Fiber also supports heart health, digestion, and weight management.
Superfoods for Diabetes
Including diabetes superfoods can improve health outcomes:
-
Chia seeds
-
Cinnamon
-
Leafy greens
-
Almonds
-
Turmeric
The Greatest Diabetes Cooking Techniques
Healthier cooking methods include:
-
Grilling
-
Baking
-
Steaming
-
Stir-frying
-
Slow cooking
These methods preserve nutrients while minimizing unhealthy fats.
FAQs About Diabetes Food PDFs and Eating with Diabetes
-
What is the best diabetes food PDF to use?
The American Diabetes Association offers the most evidence-based guide. -
Is it okay to eat fast food with diabetes?
Yes—choose grilled, high-fiber, low-sugar options. -
Where can I download a reliable diabetes food PDF?
Visit diabetes.org or McLaren’s nutrition section. -
How often should I refer to my diabetes food PDF?
Daily—for shopping, eating out, or meal prep. -
Can diabetic friendly fast food be part of my weekly plan?
Absolutely, in moderation.
Final Thoughts
Managing diabetes doesn’t have to be restrictive. By making informed food choices, practicing portion control, and using your diabetes food PDF daily, you can enjoy delicious meals while maintaining stable blood sugar levels.




